the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
In situ measurement of CO2 and CH4 from aircraft over northeast China and comparison with OCO-2 data
Xiaoyu Sun
Minzheng Duan
Yang Gao
Denghui Ji
Wenxing Zhang
Nong Chen
Xiangao Xia
Hailei Liu
Yanfeng Huo
Several satellites have been launched to monitor the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, especially CO2 and CH4 in the atmosphere, through backscattered hyperspectral radiance in the shortwave infrared (SWIR) band. The vertical profiles of greenhouse gases and aerosols could strongly affect the results from these instruments. To investigate the effects of the vertical distribution of CO2 on the uncertainty of SWIR satellite retrieval results, we conducted observations of the vertical profiles of CO2, CH4 and aerosol particles at 0.6–7 km above sea level using a Beechcraft King Air 350ER in Jiansanjiang (46.77∘ N, 131.99∘ E), Heilongjiang Province, northeast China, on 7–12 August 2018. The profiles from this aircraft captured a decrease in CO2 from 2 km to the minimum altitude due to the absorption of vegetation at the surface in summer. CH4 measurements showed about a 0.2 ppm increase from 2.0 to 0.6 km on 10 August, which may result from emissions from the large area of paddy fields below, and a constant mole fraction between 1.951 and 1.976 ppm was recorded at 2 km and above. Comparison of CO2 profiles from a new version of the carbon cycle data assimilation system Tan-Tracker (v1), retrievals from OCO-2 and aircraft measurements was conducted. The results from OCO-2 and the assimilation model system Tan-Tracker captured the vertical structure of CO2 above 3 km, whereas below 3 km the values from OCO-2 and the Tan-Tracker model were lower than those from in situ measurements. Column-averaged CO2 volume mole fractions calculated from in situ measurements showed biases of ppm () compared to OCO-2 retrievals.
- Article
(4856 KB) - Full-text XML
-
Supplement
(2572 KB) - BibTeX
- EndNote
Global warming due to greenhouse gases (GHGs) has become one of the most urgent and widely studied issues in recent years. The Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) noted that the global average temperature has increased by 0.85∘ over the period of 1880–2012. GHGs, especially the increasing CO2 levels in the atmosphere related to anthropogenic activities, are blamed for global warming, because they absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. Emission of CO2 from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes has contributed about 78 % of the total GHG emissions increase from 1970 to 2010 (IPCC, 2014). Accurate measurement of CO2 concentrations and their spatial and temporal variations in the atmosphere is essential for estimation of sources and sinks in regional and global models (Patra et al., 2005a, b; Zhang et al., 2008). The Global Atmospheric Watch program (https://community.wmo.int/activity-areas/gaw, last access: 19 June 2020) coordinates the systematic observation and analysis of GHGs and other trace substances, providing an important source of local and global GHG data. However, ground-based and in situ measurements near the surface can only provide information about the lower atmosphere and are insufficient for analysis of total-column GHGs, which exhibits variations in both the vertical and horizontal directions. Over the past few years, several satellites, including the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite (GOSAT, launched in January 2009), Second Orbiting Carbon Observatory, (OCO-2, launched in 2014) and TanSat (launched in 2016), have been launched into space to monitor CO2 by observing backscattered hyperspectral radiance in the shortwave infrared (SWIR) wavelength, which can provide global coverage of the column-averaged dry-air mole fraction of CO2 (). Studies have shown that, given a 1–2 ppm accuracy of , the use of spaceborne instrument data can reduce the uncertainties in regional ( footprint) estimation of CO2 sources and sinks (Rayner and O'Brien, 2001). In addition, CO2 vertical profiles in the 5–25 km altitude range can be obtained using limb viewing spaceborne sounders such as the Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment Fourier Transform Spectrometer (ACE-FTS, launched in August 2003). Foucher et al. (2009) reported the feasibility and difficulty of obtaining vertical CO2 profiles using this method.
To validate and calibrate the data from satellite measurement products, the Total Carbon Column Observing Network (TCCON), a network of ground-based solar Fourier transform spectrometers operating in the SWIR spectral region, was established (Wunch et al., 2011). Several studies have been conducted to determine the column-averaged volume mole fraction of CO2, CH4 and other trace gases (, and Xgas) from TCCON data, which have shown good accuracy (Hedelius et al., 2017; Mendonca et al., 2019). In addition, commercial mobile solar-viewing near-infrared spectrometers of lower resolution than the TCCON instruments, such as the Bruker™ EM27/SUN, show potential for measurement of Xgas with an acceptable bias (Hedelius et al., 2016).
Retrieval accuracy is affected by knowledge of the vertical distribution of aerosols and CO2. Vertical profiles of CO2 also affect the accuracy of estimation for regional carbon fluxes in the atmospheric transport model and can help elucidate the global carbon cycle and climate change. Many experiments have been conducted to measure the vertical profiles of CO2, CH4 and other trace gases. The AirCore sampling system can be used to obtain vertical profiles of CO2 and CH4 from near the surface to 8–12 km with high accuracy (Karion et al., 2010; Membrive et al., 2017). Active remote sensing of atmospheric with the Raman lidar (light detection and ranging) technique has been developed and used to measure CO2 vertically in the troposphere (Zhao et al., 2007; Gong et al., 2013; Han et al., 2017). CO2 concentrations were measured at 8–12 km by Tohoku University (Sendai, Japan) through flask sampling on a commercial airliner operated by Japan Airlines (JAL) between Japan and Australia in 1984 and 1985 (Nakazawa et al., 1991). The Comprehensive Observation Network for TRace gases by AIrLiner (CONTRAIL) project installed continuous CO2 measurement equipment on board aircraft operated by JAL for in situ measurement (Machida et al., 2008). The data for CONTRAIL are collected at altitudes between a few kilometers and 10 km, taking advantage of the frequent movement of commercial aircraft around the world. The Civil Aircraft for Remote Sensing and In Situ Measurements Based on the Instrumentation Container Concept (CARIBIC) project (Brenninkmeijer et al., 1999, 2007) aimed to observe trace gases such as CO, O3 and CO2 by deploying measurement equipment in passenger aircraft. The HIAPER Pole-to-Pole Observation (HIPPO) project involved a sequence of five global aircraft measurement programs to sample the atmosphere from near the north pole to the coastal waters of Antarctica (Wofsy, 2011). Direct measurements that are independently collected from the aircraft provide validation information for satellite products. Several studies have shown that profile measurements of CO2 and CH4 obtained using aircraft and AirCore are useful for bias correction of both TCCON measurements (Deutscher et al., 2010; Geibel et al., 2012; Hedelius et al., 2016; Messerschmidt et al., 2011) and satellite products (Araki et al., 2010; Inoue et al., 2013, 2014; Miyamoto et al., 2013; Frankenberg et al., 2016; Wunch et al., 2017).
Three satellites designed for CO2 measurement, TanSat (Yang et al., 2018, 2020), GMI/GF-5 (Li et al., 2016) and GAS/FY-3D (Qi et al., 2020), were launched into space in 2016, 2017 and 2018, respectively. Measurement of profiles is crucial to further validate the retrieved hyperspectral measurements from these three satellites. Because the algorithm for satellite retrieval requires a priori profiles based on the model and in situ measurements, the lack of direct and independent airborne observations may increase the bias in the satellite results over China.
In this study, in situ aircraft-based measurements of CO2 and CH4 were conducted in Jiansanjiang, northeast China, in August 2018. An ultraportable greenhouse gas analyzer (UGGA; model 915-0011; Los Gatos Research, San Jose, CA, USA) was used on board the aircraft to measure the vertical mole fractions of CO2 and CH4 at altitudes of 0.6–7 km. Descriptions of the aircraft, the onboard instruments, and the OCO-2 and Tan-tracker data used in the paper are provided in Sect. 2. Details of the experimental site and the flight trajectory are provided in Sect. 3. The data processing method including the water vapor correction is given in Sect. 4. A comparison of the profiles obtained using aircraft with OCO-2 and the assimilation system Tan-Tracker (v1) is described in Sect. 5. The methods used to calculate and extrapolate in situ profiles, as well as error estimation, are discussed in Sect. 6.
2.1 Aircraft instrumentation
The aircraft used for this experiment was a Beechcraft King Air 350ER, which is a twin-turboprop aircraft designed for weather modification missions and measurement of trace gases and aerosols by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA). The cruising speed and maximum speed of the aircraft are 441 and 561 km h−1, respectively. Temperature, wind speed, relative humidity and other meteorological data were detected and recorded by an aircraft-integrated meteorological measurement system (AIMMS-20AG) installed on the aircraft. The geolocation information including latitude, longitude, ambient pressure and height of the aircraft is also measured by the AIMMS-20AG. The relative humidity is calculated by temperature and dew point, measured by the total temperature sensor (model 102 non-de-iced, Rosemount Aerospace Inc.) and dew point hygrometer (model 137 Vigilant™, EdgeTech), respectively.
The ultraportable greenhouse gas analyzer, UGGA (model 915-0011; Los Gatos Research), was connected to an aircraft-based impactor inlet system which consists of CVI (counterflow virtual impactor inlet system, model 1204; Brechtel Manufacturing Inc.) and ISO inlet (model 1200; Brechtel Manufacturing Inc.) in the pressurized cabin for continuous measurement of CO2 and CH4. The CVI and/or ISO inlets were mounted on the top of the aircraft body as shown in Fig. 1, and the air flow rate of the inlets was kept constant by the automatic air flow controller of the inlets (aircraft-based counterflow virtual impactor inlet system CVI – model 1204, brochure; isokinetic inlet system ISO inlet – model 1200, brochure). The UGGA uses a laser absorption technology called off-axis integrated cavity output spectroscopy to determine the trace gas concentration with a high precision of <300 ppb (CO2) and <2 ppb (CH4) and a 10 s response time (UGGA user manual, model 915-0011; Los Gatos Research) and was tested and controlled in the laboratory. As shown in the in-flight schematic diagram (Fig. 1), the external oilless diaphragm vacuum pump (F-9A 08-03, GAST) was mounted between the CVI inlet and/or the ISO inlet, and it was well-designed to keep a stable airflow with the maximum flow rate of 31.15 L min−1. The ISO inlet was used as the aircraft passed through clouds, and the CVI inlet was used the other times. A similar system for airborne GHG measurement has been reported by O'Shea et al. (2013) and Palmer et al. (2013).
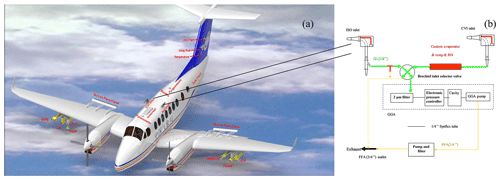
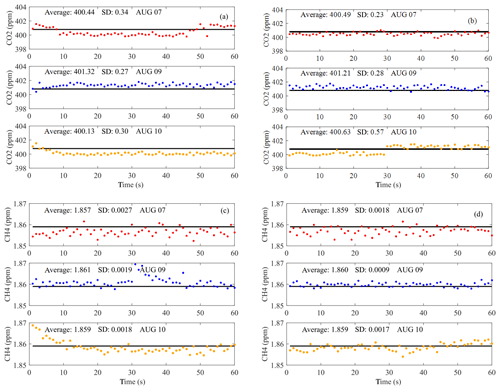
Figure 1(a) The outside view of the Beechcraft King Air 350ER instrumentation. (b) The schematic diagram of the greenhouse gas sample airflow.
During the flight, the pressure of the sample cavity was kept constant by a small pump inside the instrument with the airflow about 0.3 L min−1. The sample cavity temperature was also kept stable and constant by the temperature controller of the instrument. The instrument automatically recorded and saved the temperature and pressure in the cavity during operation. According to the records, the standard deviation of the cell pressure during three flights is 0.029, 0.029 and 0.033 on 7, 9 and 10 August, and the range of the cell pressure on each flight is below 0.16 hPa. For the cell temperature, the standard deviation is 0.46, 1.55 and 1.18 on each day and the range is below 3.11∘. The UGGA was calibrated against standard GHGs (provided by the National Institute of Metrology, China) before takeoff and after landing of each flight to ensure the accuracy of the data measured with the UGGA. Before this study, the GHG standard gases have been used by the CMA, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and other scientific research institutions for calibration and validation, showing that these standard gases have good performance and reliability. The standard gas we used is based on dry and clean air with known concentration values, filled in a 29.5 L aluminum alloy cylinder with salinization and other special treatment on the inner wall, traceable to the World Meteorological Organization Global Atmosphere Watch (WMO GAW) level 1 standard gas. The concentration of the CO2 is 400.13 ppm and CH4 is 1.867 ppm. The standard gas has been measured in the laboratory for the proportion of δ13C in CO2, and the proportion is between −8.0 ‰ and −8.2 ‰, close to the natural content, so it will not cause a significant isotopic effect on the measurement of CO2 by the optical method and meet the requirements of standard gas (Yao et al., 2013). Just before taking off, UGGA was calibrated against standard gas, and the stability of the instrument was checked and tested again using the same standard gas of CO2 and CH4 immediately after landing. As shown in Fig. 2, the concentration of CO2 and CH4 before and after landing is stable around the values of standard gas concentration, and there was almost no drift after the flight. The precision and repeatability of the instruments are also checked and tested multiple times in the laboratory, and the results show that they are stable and good for the measurements.
2.2 Tan-Tracker and OCO-2 data
Based on the nonlinear least-squares four-dimensional variational (NLS 4D-Var) data assimilation algorithm and the Goddard Earth Observing System atmospheric chemistry transport model (GEOS-Chem), Tan-Tracker provides surface flux inversion estimates and profiles of CO2 with 47 levels of vertical resolution from the surface to 0.03 hPa and horizontal resolution of . The NLS 4D-Var assimilation model Tan-Tracker (v1) and OCO-2 (v9r) retrievals are used to optimize surface terrestrial ecosystem CO2 flux and ocean CO2 flux, while prior fossil fuel emission and fire emission remain unchanged (details of model setting and prior flux information can be found in Han and Tian, 2019).
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), successfully launched on 2 July 2014, obtained global measurement of CO2 through hyperspectral measurement of reflected sunlight from Earth's atmosphere in one near-infrared (NIR) and two SWIR bands centered at 0.76, 1.61 and 2.06 µm; more details about the mission, retrieving algorithm and data characteristics can be found in Crisp et al. (2008) and O'Dell et al. (2012). The uncertainty and bias of the products related to surface properties, aerosol and cloud, and the retrieving algorithm have been reported by Butz et al. (2009), Jung et al. (2016) and Connor et al. (2016). The OCO-2 data (V9r) including , the CO2 profile and the a priori profile were used in this study.
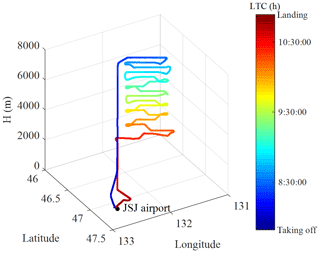
Aircraft measurements were carried out from 7 to 10 August over Jiansanjiang (47.11∘ N, 132.66∘ E, 61 m above sea level), located in Heilongjiang Province, northeast China. Figure 3 shows the geolocation of the Jiansanjiang aircraft and the flight paths. The area is mostly covered with large tracts of farmland. Rice cultivation is carried out primarily in summer, and crop growth is vigorous during this period. Due to the influence of plant photosynthesis, a large amount of CO2 uptake occurs near the surface.
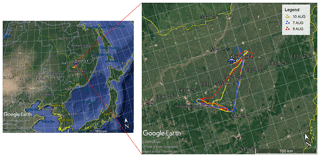
Figure 3Observation area for aircraft-based measurement of CO2 and CH4 over Jiansanjiang, northeast China, and the flight paths on 7, 9 10 August.
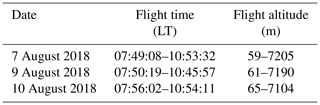
Three profiles were obtained between around 08:00 and 11:00 LT (GMT+8) on 7, 9 and 10 August 2018. The aircraft is designed for weather modification by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), so the infrastructure of the aircraft and the gas flow system is also designed and completed in the USA by the team of the weather modification agency. The CMA is in charge of the flight route, and there is a chance (more flights are planned for the future) that it can carry the greenhouse gas analyzer to measure the profiles of CO2 and CH4. The greenhouse gas analyzer was loaded on the aircraft and some parts of air flow arrangements were modified to better fit the requirement for profile measurement. Due to the logistical problem and the air traffic control restriction, we must fly in the morning from around 07:30 to 11:00 LT on these days to avoid obstructing civil aviation. The details of the three flights are listed in Table 1.
The flight trajectory on 7 August is shown in Fig. 4. The aircraft climbed up quickly and directly to the maximum height of about 7.1 km 30 min after taking off and then descended down step by step at about every 300 m. Since the 3-D figures on these 3 d look identical, the flight trajectories of the other 2 d (9 and 10 August) are not shown in Fig. 4 but available in the Supplement. Considering the sensitivity of the UGGA response, measurements during the ascent were discarded due to the rapid changes in air pressure, and only data collected while spiralling downward were regarded as valid and analyzed further. Data recorded below 0.6 km were also rejected because samples were easily contaminated with exhaust emissions during the slowing and descent of the aircraft before landing. The spiral descent of the aircraft lasted about 2.5 h on the 3 d, and the number of effective layers of measurements are 17, 21 and 20, respectively, on 7, 9 and 10 August.
4.1 Water vapor correction
The mole fraction of CO2 or CH4 measured during flight is the volume in proportion to the air containing water vapor, which cannot be directly compared with values from other data sources due to different water vapor contents of the sampled air. Therefore, the effect of water vapor is corrected and the mole fractions of CO2 and CH4 to dry air are given by
where fgas_dry (mol mol−1) is the mole fraction of a gas in dry air, and fgas (mol mol−1) is the measured mole fraction of a gas under the real air conditions with water vapor. is water vapor pressure in hectopascals, which can be calculated as
where es (hPa) is the saturated water vapor pressure at the temperature T (K) at aircraft altitudes, which can be derived from the Clausius–Clapeyron equation (Wallace and Hobbs, 2006):
where J kg−1; Mw=18.016, which is the molecular weight of water; R=8.3145 J K−1 mol−1; and es (hPa) is the saturated water vapor pressure at temperature T (K). Pressure p (hPa) of the ambient atmosphere is measured by the aircraft meteorology system, AIMMS-20AG, and the temperature T (K) was measured by total temperature sensor (model 102 type non-de-iced). The relative humidity (RH, %) was calculated by the dew point and temperature. The dew point data are obtained by a dew point hygrometer (model 137 Vigilant™, EdgeTech).
4.2 Accuracy and precision
Before the aircraft takeoff, the clocks of the UGGA, AIMMS-20AG, total temperature sensor and other instruments were adjusted to match those of the CO2, CH4 and weather system measurements, synchronizing these data to the altitude and geolocation of the aircraft. The data from UGGA and synchronous meteorology measurements, including temperature, pressure and humidity of ambient atmosphere, are recorded every second and then smoothed with a 10 s running average to further remove errors caused by temporal mismatch considering the response time of the UGGA. Because the flights followed the spiral trajectories that descended approximately every 300 m, only data collected during level flight were retained and analyzed, whereas data from the descent periods were removed to avoid the effects from vertical variations in sampling during rapid descent. The time points at the beginning and end of level flight are determined according to the altitude and its variation of the aircraft. Considering the residual time of the GHG measurement system, the data obtained 220 s from the start of the level flight are considered to be observed when the aircraft is descending rather than level, which may cause uncertainty of the measurement. Therefore, the data were kept after the level flight starting for 220 s. If the duration time of certain level flight lasted less than 220 s, the data observed during that level flight were also discarded.
The instrument was calibrated against the standard gas before and after each flight. All of the measurements during the calibration process, including the standard gas used for calibration, can trace back to the WMO scale. The maximum and the average values of the difference between the standard gas and the measurement of the instrument of each day were considered for the accuracy of the aircraft data. For the precision, note that the instrument was not continuously calibrated against the standard gas during the flight. We calculated the 1 standard deviation of the data in each level flight, and the maximum of the average value of 1σ on each day is considered to be the precision of the aircraft measurement. The accuracy of CO2 and CH4 is below 0.66 and 0.002 ppm, 0.16 % and 0.10 % of the CO2 and CH4 concentration in standard gas, respectively. For precision, the 1σ value is below 0.71 and 0.0062 ppm for CO2 and CH4, respectively.
5.1 CO2 and CH4 profiles
Figure 5 shows vertical profiles of the CO2 and CH4 mole fractions measured with the UGGA during the flight over Jiansanjiang, which is an agricultural area that produces a large amount of rice. The CO2 concentration increased with height in the troposphere (Fig. 5a), which may result from CO2 uptake by rice plants near the surface during the summer growth season. The greater increase rate of CO2 in the lower troposphere on 7 August compared to the other 2 d was probably attributed to differing weather conditions on the 3 sampling days. It was sunny on 7 August, but it was overcast on 9 and 10 August, which may have weakened photosynthesis in rice and reduced CO2 uptake. During all three flights, the maximum mole fraction of CO2 reached about 418 ppm in the free troposphere at the top of the profile.
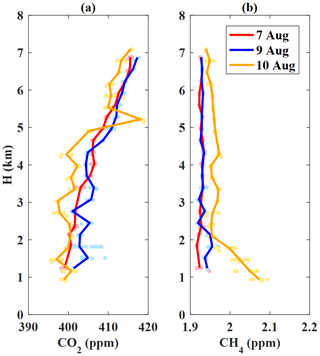
Figure 5Vertical profiles of (a) CO2 and (b) CH4 observed on 7 (blue), 9 (red) and 10 (yellow) August 2018 over Jiansanjiang measured in situ with aircraft. The aircraft-based in situ measurement data are indicated with dots, and averaged data for each flat flight stage are shown as lines.
The mole fraction of CH4 (Fig. 5b) showed a consistent decrease with increasing altitude, ranging from 1.95 to 2.10 ppm from about 2 km to near the surface, possibly as a result of CH4 emissions from agricultural activity at the surface. CH4 showed low variability of less than 0.5 ppm at higher altitudes, from above 2 to 7 km, indicating a well-mixed vertical structure of CH4 in the free troposphere.
Comparing the CO2 and CH4 observation data, the mole fraction of CH4 varied less than that of CO2 from 1.5 to 2 km up to the free troposphere, with a stable value of about 1.925 ppm, indicating that CH4 was evenly mixed at these heights and there were no obvious sources or sinks of CH4. CO2 increased with altitude in the free troposphere from about 400 to 418 ppm. This increase may have been due to photosynthesis by vegetation and the large number of crops planted locally, creating a CO2 sink at the surface and causing the CO2 concentration to rise with height in the free troposphere. The results show that the vertical profile of CO2 in summer increases with height in the upper troposphere, whereas that of CH4 changed little with height and was relatively stable over the Jiansanjiang area during the experiment.
5.2 Comparison of profiles from the model and satellite product
Aircraft measurements were compared with CO2 data obtained from OCO-2 (v9r) retrievals and the recently developed data assimilation system for the global carbon cycle, Tan-Tracker (v1) (Han and Tian, 2019). The assimilation data are collected and linearly interpolated spatially and temporally based on the geolocation of the observation site and time. Because no data were obtained from OCO-2 (v9r) over Jiansanjiang during the flight, the results of OCO-2 within spatially at the closest time to the flight were used for comparison and were collected on 5 August. The height of the profile is available on the satellite product.
The structure of CO2 varying with height could be roughly divided into three segments: the surface to 2, 2 to 3, and 3 to 8 km (Fig. 6). Below 2 km, CO2 of the Tan-Tracker model is assumed to be well-mixed and uniformly distributed with height, with values ranging from 385 to 395 ppm. Therefore, the model could not reproduce the strong decrease in CO2 from 2 km to the surface due to uptake by vegetation. From 2 to 3 km, CO2 increased to about 400 ppm with altitude. The averaged satellite retrieval profiles correctly reproduced the decrease in CO2 from 2 km to the surface, but the decrease rate was lower than those of in situ profiles, decreasing from 393 ppm at 2 km to 390 ppm near the surface. Flight data showed a significant CO2 sink in this region, most notably on 7 August when it decreased from 400 ppm at 2 km to 380 ppm at 0.6 km. The impact of ground sinks was more pronounced and apparent than that from satellite inversion and model simulations, indicating that the strong variations in the lower atmosphere and planetary boundary layer (PBL) should be more carefully considered in model and retrieval algorithms. Between 2 and 4 km, aircraft profiles showed a relatively uniform mixing level of CO2, with roughly stable concentrations around 400 ppm.
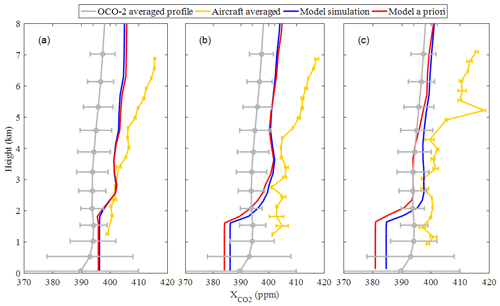
Figure 6Comparison of aircraft measurements (in situ measurement data are shown by the yellow line) with 1 standard deviation (yellow bars) collected on (a) 7, (b) 9 and (c) 10 August Tan-Tracker (v1) data (blue line) and the a priori profile of it (red line) at the location of Jiansanjiang linearly interpolated to the observation times on (a) 7, (b) 9 and (c) 10 August and the OCO-2 averaged profile (gray line) for the aircraft flight area from 5 August with 1 standard deviation (gray bars).
In general, all profiles from the aircraft, satellite retrieval and model showed a similar vertical distribution trend in the troposphere above 2 km, but with differences in values. The average of the difference between OCO-2 and the aircraft profiles above 2 km is 4.22, 8.16 and −2.57 ppm on 7, 9 and 10 August, respectively. The volume mole fraction of CO2 from both satellite and aircraft measurements indicated a CO2 sink. GHGs profiles have rarely been observed before near the experiment site, or over the northeast of China as far as we know. The model simulations are based on data of a regional emission inventory. The accuracy of simulated profiles and concentrations near the surface over the experiment site still remains unknown. Thus continuous and regular observation of the GHGs profiles are necessary for better understanding of the regional emission amounts and the variation in the GHGs.
5.3 Comparison of products
The total column amount of CO2 can be derived by integrating the CO2 concentrations from the surface to the top of the atmosphere under the assumption of hydrostatic conditions:
where is the total column amount of CO2; is the dry-air mole fraction (DMF) of CO2 (mol mol−1); is the aircraft profile of H2O (mol mol−1), which is measured by the onboard AIMMS system; m(p) is the mean molecular mass of wet air; g(p) is gravitational acceleration; kg molecule−1; kg molecule−1; and NA is Avogadro's constant. Data beyond the flight limits are taken from the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) reanalysis data interpolated to the time of flight.
The column-averaged DMF ofCO2 () from aircraft measurements was calculated based on the method of Wunch et al. (2010), which considers the average kernel in OCO-2 satellite retrievals:
where a is the average kernel (Rodgers and Connor, 2003), is the column-averaged DMF for the a priori profile ta, hj is the pressure weighting function of OCO-2 and tin situ is the in situ profile from aircraft measurement.
Because in situ measurements available from aircraft are limited, values outside the aircraft's vertical observation range must be estimated to calculate . Two extrapolation methods were used to extend the profile of the aircraft measurements and then estimate the value of the in situ measurement respectively. (1) The unknown part of the aircraft profile was directly from the OCO-2 a priori profile. (2) A well-mixed and constant mixing ratio of CO2 is assumed from the surface to the lower limit of flight and from the upper limit of flight to the tropopause. The CO2 concentrations above the tropopause were calculated with an empirical model (Toon and Wunch, 2014) which considers tropopause height as well as realistic latitude and time dependencies through curve fitting of data from high-altitude balloons, AirCore, Observations of the Middle Stratosphere balloon and aircraft. In general, the mole fraction of CO2 decreased exponentially with height from the tropopause to upper stratosphere, and the tropopause height was obtained from NCEP reanalysis data with a resolution, which was linearly interpolated to the geographic coordinates of Jiansanjiang. Figure 7 shows the extrapolated CO2 profiles using method (2).
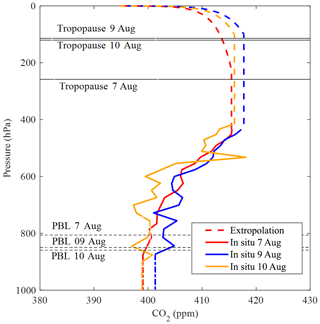
Figure 7Extrapolated CO2 profiles observed on 7, 9 and 10 August 2018, over Jiansanjiang by method (2). Red, blue and yellow solid lines show the aircraft-based (in situ) data collected on 7, 9 and 10 August, respectively, averaged for each flat stage of the flight. Dotted lines show the extrapolated parts of the profiles, with colors corresponding to sampling dates in accordance with the solid lines. Black horizontal lines show the tropopause height from NCEP reanalysis data.
calculated from the aircraft measurements and differences with that from OCO-2 are listed in Tables 2 and 3. The results showed that values of OCO-2 were lower, with an average difference of ppm () and ppm () by method (1) and by method (2).
Table 2 derived from aircraft on each observation day (7, 9 and 10 August) supplemented the aircraft profile by method (1). OCO-2 (V9r) values were from 5 August, which was the closest time point of data from OCO-2 over Jiansanjiang to the observation period. Differences between aircraft and OCO-2 are shown in the fourth (ppm) and fifth (%) columns. The average difference and standard deviation are shown in the fifth row.
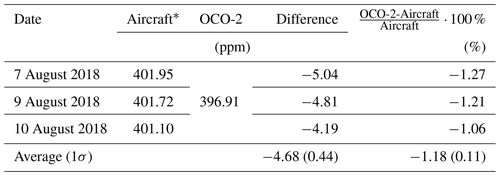
* The effect of the average kernel was taken into consideration for OCO-2.
Table 3The same as Table 2, but for method (2).
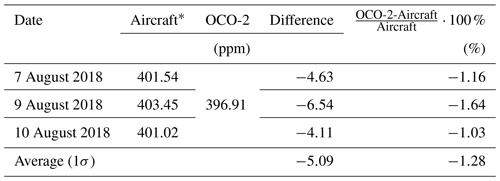
* The effect of the average kernel was taken into consideration for OCO-2.
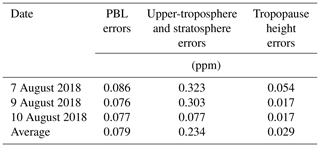
Uncertainties induced by extrapolation of profiles outside the height limits of aircraft and errors in tropopause estimation were analyzed. Errors in extrapolation of the profile below the lower limit and above the upper limit of flight were estimated by recalculating after a 1 ppm positive shift in the CO2 concentrations at these altitudes. For method (1), since the values of CO2 mole factions of the unknown part are the same as those of the OCO-2 a priori profile, as Eq. (5) shows, no extra uncertainty would be introduced by extrapolation. But for method (2), as the profile is assumed to decrease exponentially with height above the tropopause, the height of the tropopause also introduces uncertainties for . Table 4 lists the errors resulting from three sources: (1) uncertainties from in situ measurement, (2) extrapolation of the profile in the PBL where no in situ measurements were collected and (3) profile assumptions above the upper limit of flight observations. Errors due to uncertainty in tropopause height were analyzed by shifting the tropopause height upward by 1 km, and the results are also listed in Table 4. These results indicated that the extrapolation method and assumptions used to construct profiles where no measurements were made were the primary source of errors, among which the greatest error was from the profile above the upper limit of the flight (0.323 ppm). Errors due to uncertainty in the tropopause height were also non-negligible. Because of the lack of observation data near the surface, the missing measurements were directly replaced by the data at the lowest altitude measured by the aircraft. The error caused by this practice is shown in Table 4, with an average of 0.079 ppm for . This is also the impact of the lack of near-surface observations on estimation. Therefore, observations from near the surface to about 1 km from other methods, such as in situ GHG measurements by tethered balloon and high tower, are necessary for accurate estimation of .
Table 4Aircraft integration error budget of estimation for method (2). Errors in the three profiles from multiple error sources contributed to the calculation results of the integrated total column. There are four sources of error, similar to previously described error budgets (Wunch et al., 2017): the contribution from the aircraft profile itself, the contribution from the unknown surface to the bottom of the profile, the contribution from the upper troposphere and stratosphere, and error from the tropopause height.
The vertical distributions of CO2 and CH4 were measured by using a Beechcraft King Air 350ER over Jiansanjiang, an extensive paddy area in northeast China, and three vertical profiles from 0.6 to 7.5 km were obtained on 7, 9 and 10 August. Measurements of the mole fraction of CO2 showed an increase with height, whereas CH4 decreased with height. These results are reasonable, because paddies are sinks for CO2 and sources of CH4 during the summer growing season. Comparing the observed profiles from aircraft with those from the carbon cycle data assimilation system Tan-Tracker (v1) and OCO-2 retrievals showed that the general vertical structure was consistent, but the values of mole fraction of CO2 from Tan-Tracker and OCO-2 had negative bias estimates. The average bias between aircraft and OCO-2 is ppm ( %). The uncertainty mainly resulted from extrapolation of the profile beyond the flight limit, where no in situ measurements were available.
Data used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request (dmz@mail.iap.ac.cn).
The supplement related to this article is available online at: https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-13-3595-2020-supplement.
MD and XS determined the main goal of this study. XS carried it out, analyzed the data and prepared the paper with contributions from all co-authors. YG and NC provided technical guidance for related instruments.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
We also acknowledge numerous staff of the Weather Modification Center, China Meteorological Administration for supporting the experiment and the instrumentation on board the aircraft. We also thank Jiansanjiang Airport for providing the experimental site and arranging time for conducting the campaign.
This research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41527806) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41705014).
This paper was edited by Frank Hase and reviewed by three anonymous referees.
Araki, M., Morino, I., Machida, T., Sawa, Y., Matsueda, H., Ohyama, H., Yokota, T., and Uchino, O.: CO2 column-averaged volume mixing ratio derived over Tsukuba from measurements by commercial airlines, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10, 7659–7667, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-7659-2010, 2010.
Brenninkmeijer, C. A. M., Crutzen, P., Fischer, H., Güsten, H., Hans, W., Heinrich, G., Heintzenberg, J., Hermann, M., Immelmann, T., and Kersting, D.: CARIBIC–Civil aircraft for global measurement of trace gases and aerosols in the tropopause region, J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech., 16, 1373–1383, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(1999)016<1373:CCAFGM>2.0.CO;2, 1999.
Brenninkmeijer, C. A. M., Crutzen, P., Boumard, F., Dauer, T., Dix, B., Ebinghaus, R., Filippi, D., Fischer, H., Franke, H., Frieß, U., Heintzenberg, J., Helleis, F., Hermann, M., Kock, H. H., Koeppel, C., Lelieveld, J., Leuenberger, M., Martinsson, B. G., Miemczyk, S., Moret, H. P., Nguyen, H. N., Nyfeler, P., Oram, D., O'Sullivan, D., Penkett, S., Platt, U., Pupek, M., Ramonet, M., Randa, B., Reichelt, M., Rhee, T. S., Rohwer, J., Rosenfeld, K., Scharffe, D., Schlager, H., Schumann, U., Slemr, F., Sprung, D., Stock, P., Thaler, R., Valentino, F., van Velthoven, P., Waibel, A., Wandel, A., Waschitschek, K., Wiedensohler, A., Xueref-Remy, I., Zahn, A., Zech, U., and Ziereis, H.: Civil Aircraft for the regular investigation of the atmosphere based on an instrumented container: The new CARIBIC system, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 4953–4976, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-4953-2007, 2007.
Butz, A., Hasekamp, O. P., Frankenberg, C., and Aben, I.: Retrievals of atmospheric CO2 from simulated space-borne measurements of backscattered near-infrared sunlight: Accounting for aerosol effects, Appl. Optics, 48, 3322–3336, https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.48.003322, 2009.
Connor, B., Bösch, H., McDuffie, J., Taylor, T., Fu, D., Frankenberg, C., O'Dell, C., Payne, V. H., Gunson, M., Pollock, R., Hobbs, J., Oyafuso, F., and Jiang, Y.: Quantification of uncertainties in OCO-2 measurements of XCO2: simulations and linear error analysis, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 5227–5238, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-9-5227-2016, 2016.
Crisp, D., Miller, C. E., and DeCola, P. L.: NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory: measuring the column averaged carbon dioxide mole fraction from space, J. Appl. Remote Sens., 2, 023508, https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2898457, 2008.
Deutscher, N. M., Griffith, D. W. T., Bryant, G. W., Wennberg, P. O., Toon, G. C., Washenfelder, R. A., Keppel-Aleks, G., Wunch, D., Yavin, Y., Allen, N. T., Blavier, J.-F., Jiménez, R., Daube, B. C., Bright, A. V., Matross, D. M., Wofsy, S. C., and Park, S.: Total column CO2 measurements at Darwin, Australia – site description and calibration against in situ aircraft profiles, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 3, 947–958, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-3-947-2010, 2010.
Foucher, P. Y., Chédin, A., Dufour, G., Capelle, V., Boone, C. D., and Bernath, P.: Technical Note: Feasibility of CO2 profile retrieval from limb viewing solar occultation made by the ACE-FTS instrument, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 2873–2890, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-2873-2009, 2009.
Frankenberg, C., Kulawik, S. S., Wofsy, S. C., Chevallier, F., Daube, B., Kort, E. A., O'Dell, C., Olsen, E. T., and Osterman, G.: Using airborne HIAPER Pole-to-Pole Observations (HIPPO) to evaluate model and remote sensing estimates of atmospheric carbon dioxide, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16, 7867–7878, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-7867-2016, 2016.
Geibel, M. C., Messerschmidt, J., Gerbig, C., Blumenstock, T., Chen, H., Hase, F., Kolle, O., Lavrič, J. V., Notholt, J., Palm, M., Rettinger, M., Schmidt, M., Sussmann, R., Warneke, T., and Feist, D. G.: Calibration of column-averaged CH4 over European TCCON FTS sites with airborne in-situ measurements, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 8763–8775, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-8763-2012, 2012.
Gong, W., Han, G., Ma, X., and Lin, H.: Multi-points scanning method for wavelength locking in CO2 differential absorption lidar, Opt. Commun., 305, 180–184, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2013.05.006, 2013.
Han, G., Ma, X., Liang, A., Zhang, T., Zhao, Y., Zhang, M., and Gong, W.: Performance evaluation for China's planned CO2-IPDA, Remote Sens., 9, 768, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080768, 2017.
Han, R. and Tian, X.: A dual-pass carbon cycle data assimilation system to estimate surface CO2 fluxes and 3D atmospheric CO2 concentrations from spaceborne measurements of atmospheric CO2, Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-2019-54, in review, 2019.
Hedelius, J. K., Viatte, C., Wunch, D., Roehl, C. M., Toon, G. C., Chen, J., Jones, T., Wofsy, S. C., Franklin, J. E., Parker, H., Dubey, M. K., and Wennberg, P. O.: Assessment of errors and biases in retrievals of , , XCO, and from a 0.5 cm−1 resolution solar-viewing spectrometer, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 3527–3546, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-9-3527-2016, 2016.
Hedelius, J. K., Parker, H., Wunch, D., Roehl, C. M., Viatte, C., Newman, S., Toon, G. C., Podolske, J. R., Hillyard, P. W., Iraci, L. T., Dubey, M. K., and Wennberg, P. O.: Intercomparability of XCO2 and XCH4 from the United States TCCON sites, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 10, 1481–1493, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-10-1481-2017, 2017.
Inoue, M., Morino, I., Uchino, O., Miyamoto, Y., Yoshida, Y., Yokota, T., Machida, T., Sawa, Y., Matsueda, H., Sweeney, C., Tans, P. P., Andrews, A. E., Biraud, S. C., Tanaka, T., Kawakami, S., and Patra, P. K.: Validation of XCO2 derived from SWIR spectra of GOSAT TANSO-FTS with aircraft measurement data, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 9771–9788, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-9771-2013, 2013.
Inoue, M., Morino, I., Uchino, O., Miyamoto, Y., Saeki, T., Yoshida, Y., Yokota, T., Sweeney, C., Tans, P. P., Biraud, S. C., Machida, T., Pittman, J. V., Kort, E. A., Tanaka, T., Kawakami, S., Sawa, Y., Tsuboi, K., and Matsueda, H.: Validation of XCH4 derived from SWIR spectra of GOSAT TANSO-FTS with aircraft measurement data, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 7, 2987–3005, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-7-2987-2014, 2014.
IPCC: Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report, Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, edited by: Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R. K., and Meyer, L. A., IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland, 151 pp., 2014.
Jung, Y., Kim, J., Kim, W., Boesch, H., Lee, H., Cho, C., and Goo, T.-Y.: Impact of aerosol property on the accuracy of a CO2 retrieval algorithm from satellite remote sensing, Remote Sens., 8, 322, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8040322, 2016.
Karion, A., Sweeney, C., Tans, P., and Newberger, T.: AirCore: An innovative atmospheric sampling system, J. Atmos. Ocean Tech., 27, 1839–1853, https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JTECHA1448.1, 2010.
Li, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, D., Chen, J., Rong, P., Zhang, X., and Wang, S.: CO2 retrieval model and analysis in short-wave infrared spectrum, Optik, 127, 4422–4425, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.01.144, 2016.
Machida, T., Matsueda, H., Sawa, Y., Nakagawa, Y., Hirotani, K., Kondo, N., Goto, K., Nakazawa, T., Ishikawa, K., and Ogawa, T.: Worldwide measurements of atmospheric CO2 and other trace gas species using commercial airlines, J. Atmos. Ocean Tech., 25, 1744–1754, https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JTECHA1082.1, 2008.
Membrive, O., Crevoisier, C., Sweeney, C., Danis, F., Hertzog, A., Engel, A., Bönisch, H., and Picon, L.: AirCore-HR: a high-resolution column sampling to enhance the vertical description of CH4 and CO2, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 10, 2163–2181, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-10-2163-2017, 2017.
Mendonca, J., Strong, K., Wunch, D., Toon, G. C., Long, D. A., Hodges, J. T., Sironneau, V. T., and Franklin, J. E.: Using a speed-dependent Voigt line shape to retrieve O2 from Total Carbon Column Observing Network solar spectra to improve measurements of XCO2, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 12, 35–50, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-35-2019, 2019.
Messerschmidt, J., Geibel, M. C., Blumenstock, T., Chen, H., Deutscher, N. M., Engel, A., Feist, D. G., Gerbig, C., Gisi, M., Hase, F., Katrynski, K., Kolle, O., Lavrič, J. V., Notholt, J., Palm, M., Ramonet, M., Rettinger, M., Schmidt, M., Sussmann, R., Toon, G. C., Truong, F., Warneke, T., Wennberg, P. O., Wunch, D., and Xueref-Remy, I.: Calibration of TCCON column-averaged CO2: the first aircraft campaign over European TCCON sites, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, 10765–10777, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-10765-2011, 2011.
Miyamoto, Y., Inoue, M., Morino, I., Uchino, O., Yokota, T., Machida, T., Sawa, Y., Matsueda, H., Sweeney, C., Tans, P. P., Andrews, A. E., and Patra, P. K.: Atmospheric column-averaged mole fractions of carbon dioxide at 53 aircraft measurement sites, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 5265–5275, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-5265-2013, 2013.
Nakazawa, T., Miyashita, K., Aoki, S., and Tanaka, M.: Temporal and spatial variations of upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric carbon dioxide, Tellus B, 43, 106–117, https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v43i2.15254, 1991.
O'Dell, C. W., Connor, B., Bösch, H., O'Brien, D., Frankenberg, C., Castano, R., Christi, M., Eldering, D., Fisher, B., Gunson, M., McDuffie, J., Miller, C. E., Natraj, V., Oyafuso, F., Polonsky, I., Smyth, M., Taylor, T., Toon, G. C., Wennberg, P. O., and Wunch, D.: The ACOS CO2 retrieval algorithm – Part 1: Description and validation against synthetic observations, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 5, 99–121, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-5-99-2012, 2012.
O'Shea, S. J., Bauguitte, S. J.-B., Gallagher, M. W., Lowry, D., and Percival, C. J.: Development of a cavity-enhanced absorption spectrometer for airborne measurements of CH4 and CO2, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 6, 1095–1109, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-6-1095-2013, 2013.
Palmer, P. I., Parrington, M., Lee, J. D., Lewis, A. C., Rickard, A. R., Bernath, P. F., Duck, T. J., Waugh, D. L., Tarasick, D. W., Andrews, S., Aruffo, E., Bailey, L. J., Barrett, E., Bauguitte, S. J.-B., Curry, K. R., Di Carlo, P., Chisholm, L., Dan, L., Forster, G., Franklin, J. E., Gibson, M. D., Griffin, D., Helmig, D., Hopkins, J. R., Hopper, J. T., Jenkin, M. E., Kindred, D., Kliever, J., Le Breton, M., Matthiesen, S., Maurice, M., Moller, S., Moore, D. P., Oram, D. E., O'Shea, S. J., Owen, R. C., Pagniello, C. M. L. S., Pawson, S., Percival, C. J., Pierce, J. R., Punjabi, S., Purvis, R. M., Remedios, J. J., Rotermund, K. M., Sakamoto, K. M., da Silva, A. M., Strawbridge, K. B., Strong, K., Taylor, J., Trigwell, R., Tereszchuk, K. A., Walker, K. A., Weaver, D., Whaley, C., and Young, J. C.: Quantifying the impact of BOReal forest fires on Tropospheric oxidants over the Atlantic using Aircraft and Satellites (BORTAS) experiment: design, execution and science overview, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 6239–6261, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-6239-2013, 2013.
Patra, P. K., Maksyutov, S., Ishizawa, M., Nakazawa, T., Takahashi, T., and Ukita, J.: Interannual and decadal changes in the sea-air CO2 flux from atmospheric CO2 inverse modeling, Global Biogeochem. Cy., 19, GB4013, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GB002257, 2005a.
Patra, P. K., Ishizawa, M., Maksyutov, S., Nakazawa, T., and Inoue, G.: Role of biomass burning and climate anomalies for land-atmosphere carbon fluxes based on inverse modeling of atmospheric CO2, Global Biogeochem. Cy., 19, GB3005, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GB002258, 2005b.
Qi, C., Wu, C., Hu, X., Xu, H., Lee, L., Zhou, F., Gu, M., Yang, T., Shao, C., and Yang, Z.: High spectral infrared atmospheric sounder (HIRAS): system overview and on-orbit performance assessment, IEEE T. Geosci. Remote, 58, 4335–4352, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2963085, 2020.
Rayner, P. and O'Brien, D.: The utility of remotely sensed CO2 concentration data in surface source inversions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 175–178, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL011912, 2001.
Rodgers, C. D. and Connor, B. J.: Intercomparison of remote sounding instruments, J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4116, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002299, 2003.
Toon, G. C. and Wunch, D.: A stand-alone a priori profile generation tool for GGG2014 release, TCCON data archive, hosted by the Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA, https://doi.org/10.14291/tccon.ggg2014.priors.r0/1221661, 2014.
Wallace, J. M. and Hobbs, P. V.: Atmospheric science: an introductory survey, Elsevier, New York, 2006.
Wofsy, S. C.: HIAPER Pole-to-Pole Observations (HIPPO): fine-grained, global-scale measurements of climatically important atmospheric gases and aerosols, Philos. T. Roy. Soc. A, 369, 2073–2086, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2010.0313, 2011.
Wunch, D., Toon, G. C., Blavier, J.-F. L., Washenfelder, R. A., Notholt, J., Connor, B. J., Griffith, D. W., Sherlock, V., and Wennberg, P. O.: The total carbon column observing network, Philos. T. Roy. Soc. A, 369, 2087–2112, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2010.0240, 2011.
Wunch, D., Toon, G. C., Wennberg, P. O., Wofsy, S. C., Stephens, B. B., Fischer, M. L., Uchino, O., Abshire, J. B., Bernath, P., Biraud, S. C., Blavier, J.-F. L., Boone, C., Bowman, K. P., Browell, E. V., Campos, T., Connor, B. J., Daube, B. C., Deutscher, N. M., Diao, M., Elkins, J. W., Gerbig, C., Gottlieb, E., Griffith, D. W. T., Hurst, D. F., Jiménez, R., Keppel-Aleks, G., Kort, E. A., Macatangay, R., Machida, T., Matsueda, H., Moore, F., Morino, I., Park, S., Robinson, J., Roehl, C. M., Sawa, Y., Sherlock, V., Sweeney, C., Tanaka, T., and Zondlo, M. A.: Calibration of the Total Carbon Column Observing Network using aircraft profile data, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 3, 1351–1362, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-3-1351-2010, 2010.
Wunch, D., Wennberg, P. O., Osterman, G., Fisher, B., Naylor, B., Roehl, C. M., O'Dell, C., Mandrake, L., Viatte, C., Kiel, M., Griffith, D. W. T., Deutscher, N. M., Velazco, V. A., Notholt, J., Warneke, T., Petri, C., De Maziere, M., Sha, M. K., Sussmann, R., Rettinger, M., Pollard, D., Robinson, J., Morino, I., Uchino, O., Hase, F., Blumenstock, T., Feist, D. G., Arnold, S. G., Strong, K., Mendonca, J., Kivi, R., Heikkinen, P., Iraci, L., Podolske, J., Hillyard, P. W., Kawakami, S., Dubey, M. K., Parker, H. A., Sepulveda, E., García, O. E., Te, Y., Jeseck, P., Gunson, M. R., Crisp, D., and Eldering, A.: Comparisons of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) measurements with TCCON, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 10, 2209–2238, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-10-2209-2017, 2017.
Yang, Z., Zhen, Y., Yin, Z., Lin, C., Bi, Y., Liu, W., Wang, Q., Wang, L., Gu, S., and Tian, L.: Prelaunch radiometric calibration of the tansat atmospheric carbon dioxide grating spectrometer, IEEE T. Geosci. Remote, 56, 4225–4233, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2829224, 2018.
Yang, Z., Bi, Y.-M., Wang, Q., Liu, C.-B., Gu, S.-Y., Zheng, Y., Lin, C., Yin, Z., and Tian, L.: Inflight Performance of the TanSat Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Grating Spectrometer, IEEE T. Geosci. Remote, 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966113, 2020.
Yao, B., Huang, J., Zhou, L., Fang, S., Liu, L., Xia, L., Li, P., and Wang, H.: Preparation of mixed standards for high accuracy measurements, Environ. Chem., 2, 307–312, 2013 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yevich, R. and Logan, J. A.: An assessment of biofuel use and burning of agricultural waste in the developing world, Global Biogeochem. Cy., 17, 1095, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GB001952, 2003.
Zhang, D., Tang, J., Shi, G., Nakazawa, T., Aoki, S., Sugawara, S., Wen, M., Morimoto, S., Patra, P. K., and Hayasaka, T.: Temporal and spatial variations of the atmospheric CO2 concentration in China, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L03801, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032531, 2008.
Zhao, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Yuefeng, Z., Su, J., Fang, X., Cao, K., Xie, J., and Du, X.: Analysis of influence of atmosphere extinction to Raman lidar monitoring CO2 concentration profile, Chin. Phys., 16, 2486, https://doi.org/10.1088/1009-1963/16/8/055, 2007.