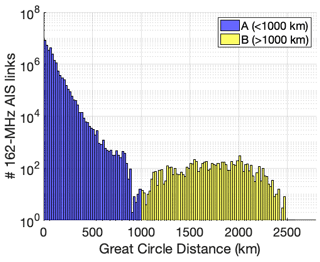
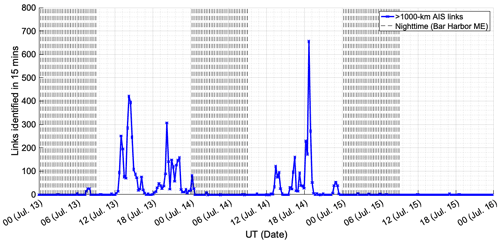
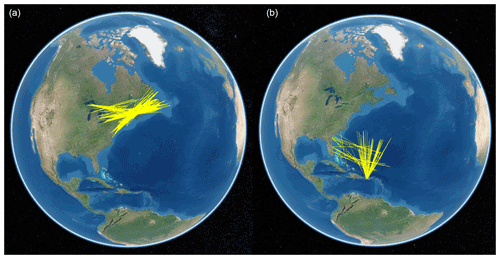
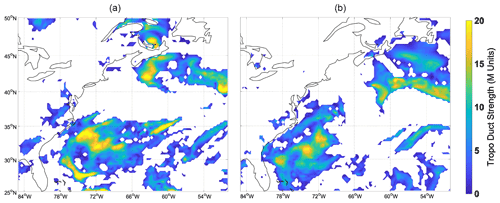
Ames, L. A., Newman, P., and Rogers, T. F.: VHF tropospheric overwater
measurements far beyond the radio horizon, Proceedings of the IRE, 43, 1369–1373, 1955.
Arras, C. and Wickert, J.: Estimation of ionospheric sporadic E
intensities from GPS radio occultation measurements, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phy., 171, 60–63, 2018.
Carmona, R. A., Nava, O. A., Dao, E. V., and Emmons, D. J.: A Comparison of
Sporadic-E Occurrence Rates Using GPS Radio Occultation and Ionosonde
Measurements, Remote Sens., 14, 581, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030581, 2022.
Chandra, H. and Rastogi, R. G.: Blanketing sporadic E layer near the
magnetic equator, J. Geophys. Res., 80, 149–153, 1975.
Chartier, A.: Long distance AIS links associated with sporadic-E, YouTube [video], https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AcNzM03zZP8, last access: 3 November 2022a.
Chartier, A. T.: AMT sporadic E paper code release, Zenodo [code], https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7278089, 2022b.
Chu, Y. H., Wang, C. Y., Wu, K. H., Chen, K. T., Tzeng, K. J., Su, C. L.,
and Plane, J. M. C.: Morphology of sporadic E layer retrieved from
COSMIC GPS radio occultation measurements: Wind shear theory examination.
J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys., 119, 2117–2136, 2014.
Deacon, C., Mitchell, C., and Watson, R.: Consolidated Amateur Radio Signal
Reports as Indicators of Intense Sporadic E Layers, Atmosphere, 13, 906,
https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060906, 2022.
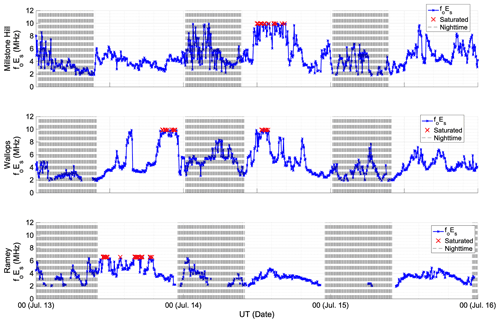
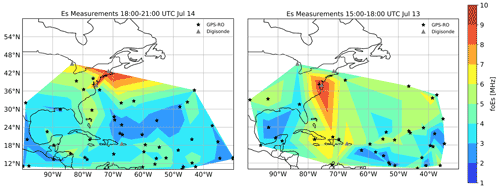
Emmons, D.: GNSS and Digisonde sporadic-E maps produced by Air Force Institute of Technology, Zenodo [data set], https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6977022, 2022.
Global Ionosphere Radio Observatory: FastChar – Digital Ionogram Data Base (DIDBase), GIRO [data set], http://giro.uml.edu/didbase/scaled.php, last access: 3 November 2022.
Gooch, J. Y., Colman, J. J., Nava, O. A., and Emmons, D. J.: Global
ionosonde and GPS radio occultation sporadic-E intensity and height
comparison, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phy., 199, 105200, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2020.105200, 2020.
Haldoupis, C.: A tutorial review on sporadic E layers, Aeronomy of the Earth's Atmosphere and Ionosphere, 381–394, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0326-1_29, 2011.
Han, R.-Y.: A Study of The Secant Law for Sporadic E, All Graduate Theses
and Dissertations, 3322,
https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd/3322 (last access: 3 November 2022), 1970.
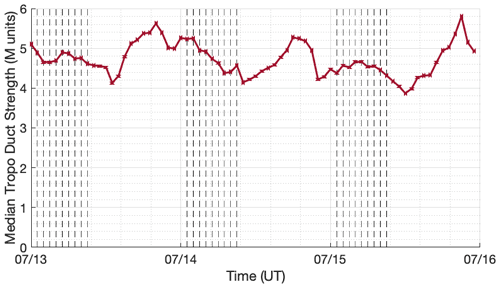
Hanley, T. R. and Chartier, A. T.: Tropospheric ducting maps, Zenodo [data set], https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7140002, 2022.
Hersbach, H., Bell, B., Berrisford, P., Biavati, G., Horányi, A.,
Muñoz Sabater, J., Nicolas, J., Peubey, C., Radu, R., Rozum, I.,
Schepers, D., Simmons, A., Soci, C., Dee, D., and Thépaut, J-N.: ERA5 hourly
data on pressure levels from 1959 to present, Copernicus Climate Change
Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS), https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.bd0915c6, 2018.
International Maritime Organization: AIS Transponders,
https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Safety/Pages/AIS.aspx, last access: 1 June
2022.
Maeda, J. and Heki, K.: Two-dimensional observations of midlatitude
sporadic E irregularities with a dense GPS array in Japan, Radio Sci., 49, 28–35,
2014.
Maruyama, T., Kato, H., and Nakamura, M.: Meteor-induced transient sporadic
E as inferred from rapid-run ionosonde observations at
midlatitudes, J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys., 113, A9, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013362, 2008.
Mathews, J. D.: Sporadic E: current views and recent progress,
J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phy., 60, 413–435, 1998.
Sampol, G.: 144 MHz Sporadic-E QSO maps. Years 2003 to 2021, https://www.dxmaps.com/esmaps/oldesmaps.html, last access: 10 June
2022.
Shinagawa, H., Tao, C., Jin, H., Miyoshi, Y., and Fujiwara, H.: Numerical
prediction of sporadic E layer occurrence using GAIA, Earth Planets Space, 73, 1–18, 2021.
Stambovsky, D. W., Colman, J. J., Nava, O. A., and Emmons, D. J.:
Simulation of GPS radio occultation signals through Sporadic-E using the
multiple phase screen method., J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr.
Phy., 214, 105538, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2021.105538, 2021.
Thomas, J. A. and Smith, E. K.: A survey of the present knowledge of
sporadic-E ionization, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr.
Phy., 13, 295–314, 1959.
UCAR COSMIC Program: COSMIC-2 Data Products, UCAR [data set], https://doi.org/10.5065/t353-c093, 2019.
Whitehead, J. D.: Production and prediction of sporadic E, Rev. Geophys., 8, 65–144,
1970.
Wu, D. L., Ao, C. O., Hajj, G. A., de La Torre Juarez, M., and Mannucci, A.
J.: Sporadic E morphology from GPS-CHAMP radio occultation, J. Geophys. Res.-Space Phys., 110, A01306, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JA010701, 2005.
Yamazaki, Y., Arras, C., Andoh, S., Miyoshi, Y., Shinagawa, H., Harding, B.
J., Englert, C. R., Immel, T. J., Sobhkhiz-Miandehi, S.,
and Stolle, C.: Examining the Wind Shear Theory of Sporadic E with
ICON/MIGHTI Winds and COSMIC-2 Radio Occultation Data, Geophys. Res. Lett., 49, e2021GL096202, https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL096202,
2022.
Yu, B., Scott, C. J., Xue, X., Yue, X., and Dou, X.: Derivation of global
ionospheric Sporadic E critical frequency (fo Es) data from the amplitude
variations in GPS/GNSS radio occultations, Roy. Soc. Open Sci., 7, 200320, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200320, 2020.